Scientists trace the effect of plasma formation on the dynamics of astrophysical jets from the celestial body
jatinnews.com July 8, 2024 0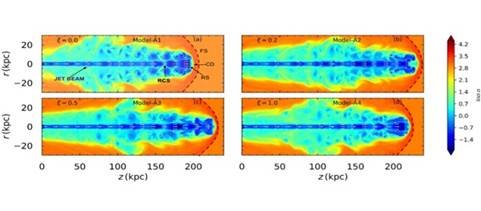
Scientists have detected the effect of the plasma formation of astrophysical jets flowing ionized matter emitted as beams extending from celestial objects such as black holes, neutron stars and pulsars.
Despite years of research, it is not known what kind of materials are made up of astrophysical jets — whether they are made up of empty electrons or protons, or whether positively charged electrons are also present. Knowing the jet structure is very important as it will allow the identification of real physical processes when operating near black holes and neutron stars. In general, theoretical studies do not have information on the structure in the relationship between thermodynamic quantities of jets such as mass density, energy density, and pressure. Such a relation is called the equation of state of jet matter.
Scientists at the Aryabhatta Research Institute of Observation Science (AAC)
Scientists at the Aryabhatta Research Institute of Observation Science (AAC), an autonomous body of the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India, used a relativistic equation of state, which they had proposed in an earlier paper on the role of the structure of relativistic plasma in the actual evolution of jet.
The research, led by Raj Kishore Joshi and Dr Indranil Chattopadhyay of ARAC, has been published in the Estrophysical Journal (APJ). The authors upgraded a numerical simulation code previously developed by Dr. Chattopadhyay, using the above equations of state to study the dynamics of astrophysical jets formed by combining electrons, positrons (positively charged electrons) and protons.

Density outline of jets with different plasma formations (φ is the ratio of proton and electron number density)
Figure: Density outline of jets with different plasma formations (φ is the ratio of proton and electron number density). The propagation direction of the jet is z (in kilo parsec or kpc) and the lateral extension is in the radial (r) direction. The initial parameters (initial Lorentz factor γ =10, density of jet beam =1.0, pressure p =0.02) have been kept the same for all models (models A1-A4). It is traveling through an environment 10 times more condensed than Jet. Forward shock (FS), jet-head or contact (CD) reverse shock (RS) and one resolution shock (RCS) surface have been marked. ξ=0 (Model A1) is the electron-positron pair jet, ξ=1.0 (Model A4) is the electron-proton jet. The electron-positron jet is the slowest jet
Jets composed of electrons and positrons were found to be the slowest compared to jets with protons opposite to expectation
The authors point out that changes in plasma structure cause differences in the propagation velocity of the jets even if the initial parameters of the jets remain the same. Jets composed of electrons and positrons were found to be the slowest compared to jets with protons opposite to expectation. Protons are about two thousand times more massive than electrons or positrons.
It is important to understand the plasma structure of the jet because the change in the plasma structure changes the internal energy of the jet which is reflected in the change in the propagation velocity. In addition, the plasma structure also affects the jet structure such as the number and strength of the recombinant shocks, the shape and dynamics of the reverse shock, etc. The reconnected shock is the region in the jet beam that is created due to the interaction of the jet beam with the backflowing material.
The plasma structure also affects the jet structure such as the number and strength of the recombinant shocks
It is important to understand the plasma structure of the jet because the change in the plasma structure changes the internal energy of the jet which is reflected in the change in the propagation velocity. In addition, the plasma structure also affects the jet structure such as the number and strength of the recombinant shocks, the shape and dynamics of the reverse shock, etc. The reconnected shock is the region in the jet beam that is created due to the interaction of the jet beam with the backflowing material.
Electron-positron jets show a more pronounced turbulent pattern. The growth of these patterns also results in the degradation of the planes. The formation and growth of turbulent patterns are known to affect the stability of the jets. Therefore, plasma formation can also affect the long-term stability of the jet. read more

